The Europe payments and finance regulatory environment keeps on changing. In recent years, the United Kingdom and European countries have seen new laws introduced.
The fintech industry is growing very fast in Europe and it needs to be checked to ensure they operate in a secure environment. Europe makes up 17% of the global cumulative valuation of fintech (around USD 2.26 trillion), its largest venture capital investment category receiving 20% of all venture capital in Europe: a higher percentage than in Asia and the United States.
Comprehensive laws have been brought forward to protect the customers affecting all European businesses and other nations outside Europe.
Businesses and merchants must comply with the regulatory bodies to ensure efficient operations no matter how intimidating it might seem to abide by the payments and finance regulations set by the European governments.
Some of the notable laws include:
Payment Services Directive (PSD2)
Payment directive 2 provides the legal foundation for further developing a better integrated internal market for electronic payments within the European Union (EU). It is aimed at increasing the security of online payments.
Merchants and financial institutions are required to adhere to strict security requirements for all online transactions. The businesses have to apply the most recent versions of 3DS 2 in Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) to offer protection and liability guarantees.
This law is meant to spur the fintech industry’s growth, which could provide innovative services that could rival traditional financial institutions.
The law requires merchants and businesses to be transparent, adhere to strict security requirements, and uphold the rights and obligations of customers
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a legal framework that aims to give European consumers more control over their data.
The law requires merchants and businesses to seek consent when collecting personal data from customers. Businesses are also under an obligation to protect the data from misuse which can lead to fraud and cyber-attacks.
Non-compliance attracts fines of up to €2.0 million or 4% of annual global revenue.
Data protection officers are recommended within the business in the EU. If the organization is outside of the EU, then there is a requirement to appoint a representative within the country where the personal data is being collected.
Consumer Rights Directive (CRD)
CRD law intends to harmonize all consumer protection rights across Europe when they purchase goods and services.
The law protects consumers’ right to accurate and clear information, right to repair or replacement, right to compensation, and right to withdraw from a distance contract among other consumer rights. The payment merchants are obliged to provide maximum human rights to the consumers.
To build consumer confidence and trust, payments businesses have to comply with the directive.
Electronic Money Directive (EMD2)
The law provides the legal framework for merchants offering e-money products to operate within. The EMD requires e-money platforms and merchants to maintain adequate levels of capital, protect customer funds, and report all their activities to the relevant regulatory authorities.
To operate in the Europe market, e-money merchants must be authorized as an e-money issuers. EU and national laws are applied in determining the compliance of the companies.
Companies must meet all the security(GDPR) check and compliance for them to be licensed to operate in the EU market. Electronic money institutions must inform the relevant authorities on how they safeguard funds that have been received in exchange for electronic money issued.
Nations that are members require electronic money institutions to hold, at the time of authorization, an initial capital of not less than EUR 350 000.
Interchange Fee Regulation (IFR)
This law aims at regulating fees charged by card issuers when a cardholder uses their debit or credit card to make payments.
The interchange fees for consumer debit card transactions are capped at 0.2% of the transaction value, while interchange fees for consumer credit card transactions are capped at 0.3% of the transaction value. Cross-border and assessment fees can be included.
Fees charged should be monitored and reported so that there can be transparency and a level playground established in the payment ecosystem and thus promoting the use of electronic money across Europe.
Capital Requirement Directive (CRD iv)
The law provides rules and standards for the regulation and supervision of banks and investment companies in the EU.
The directive is part of the EU’s ongoing efforts to reform the financial sector and promote financial stability, following the global financial crisis that was witnessed in 2020 and 2022.
Payment companies and financial institutions must ensure they have enough capital, invest in risk management technology, and must have proper governance.
Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD)
In the wake of Russia sanctions and increased threats of terrorism, Europe has increased its AMLD laws in recent years. The directive provides a framework for the prevention, detection, and reporting of money laundering and terrorist financing activities, with the ultimate goal of protecting the EU’s financial system from these threats.
The laws and directives require financial companies and payment providers to do customer due diligence and KYC, risk management, and report any suspicious transactions to the relevant authorities within the operating state.
It is meant to facilitate collaboration and coordination between anti-money laundering authorities and terrorist tracking authorities.
Transaction Value of each of the targeted Segments by the Payments and Financial Laws
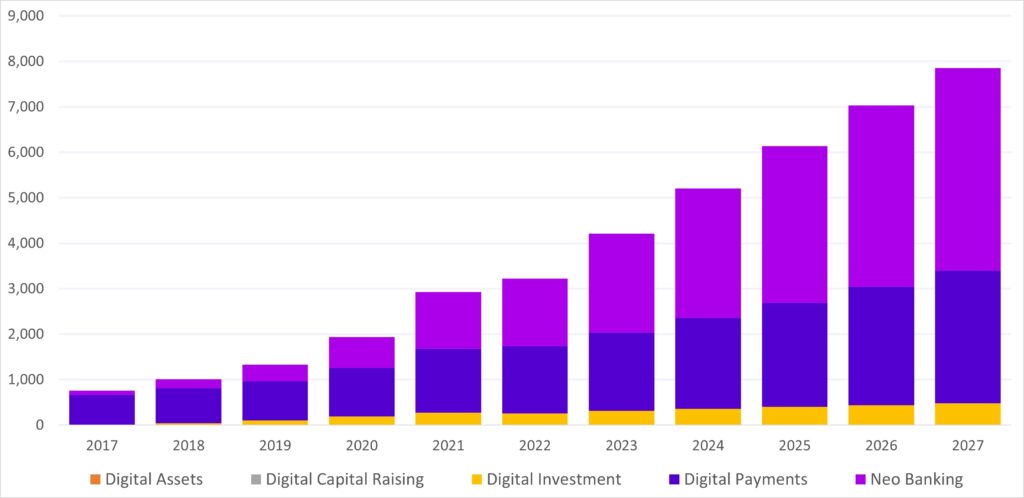
- The market’s largest segment will be Neobanking with a total transaction value of US$2,172.00bn in 2023.
- The Neobanking segment is expected to show a revenue growth of 31.2% in 2024. Total Transaction Value in the Neobanking segment is projected to be US$2,172.00bn in 2023.
Conclusion
The European Union and the UK are taking comprehensive steps in regulating the ever-changing payments and financial markets. The current laws are leaning towards consumer protection and require payments businesses to be consumers centric.
These laws are creating a level playing ground for industry players in the payments and finance market. Safety and security in the online payments and financial market are important among member states.
Sources:
[1] https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/europe-fintech-market
[2] https://eur-lex.europa.eu/EN/legal-content/summary/revised-rules-for-payment-services-in-the-eu.html
[3] https://www.gdpreu.org/gdpr-compliance/
[4] https://commission.europa.eu/law/law-topic/consumer-protection-law/consumer-contract-law/consumer-rights-directive_en
[5] https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2009/110/oj
[6] https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX%3A32015R0751
[7] https://www.europex.org/eulegislation/crd-iv-and-crr/
[8] https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32015L0849
[9] https://www.statista.com/outlook/dmo/fintech/europe